The metaversum, often referred to as the “next internet” is a virtual world where users can interact with other participants and the digital environment, thanks to appropriate tools in the form of VR goggles or haptic gloves. Although it is mainly associated with the Meta platform or Microsoft, its benefits are being recognized by an increasing number of industrial companies.
What is an industry metaverse?
The metaversum is a network of interacting digital twins that are faithful reflections of their counterparts in the physical world. As one of the essential components of Industry 4.0, it is used to simulate real, existing or planned production lines, factories or even entire logistics and distribution centers. Since this type of environment ensures complete safety, and the processes taking place there are 100% controlled, it opens up endless possibilities for various types of modifications and product testing. In addition, the meta-world is also used for training employees, for example, in machine operation or analyzing the parameters of their work, thus supporting the development of robotization and automation of production. In this context, the metaversum is becoming a new working environment for many entities operating in the automotive industry.
How can the metaversum change the automotive industry?
The metaversum has the potential to revolutionize the automotive industry in many ways. Not only does it enable automakers to test and cost-effectively optimize their designs in a secure, virtual environment, but it may also irreversibly change the standards of customer service – both in B2B and B2C relationships.
Development of autonomous vehicles
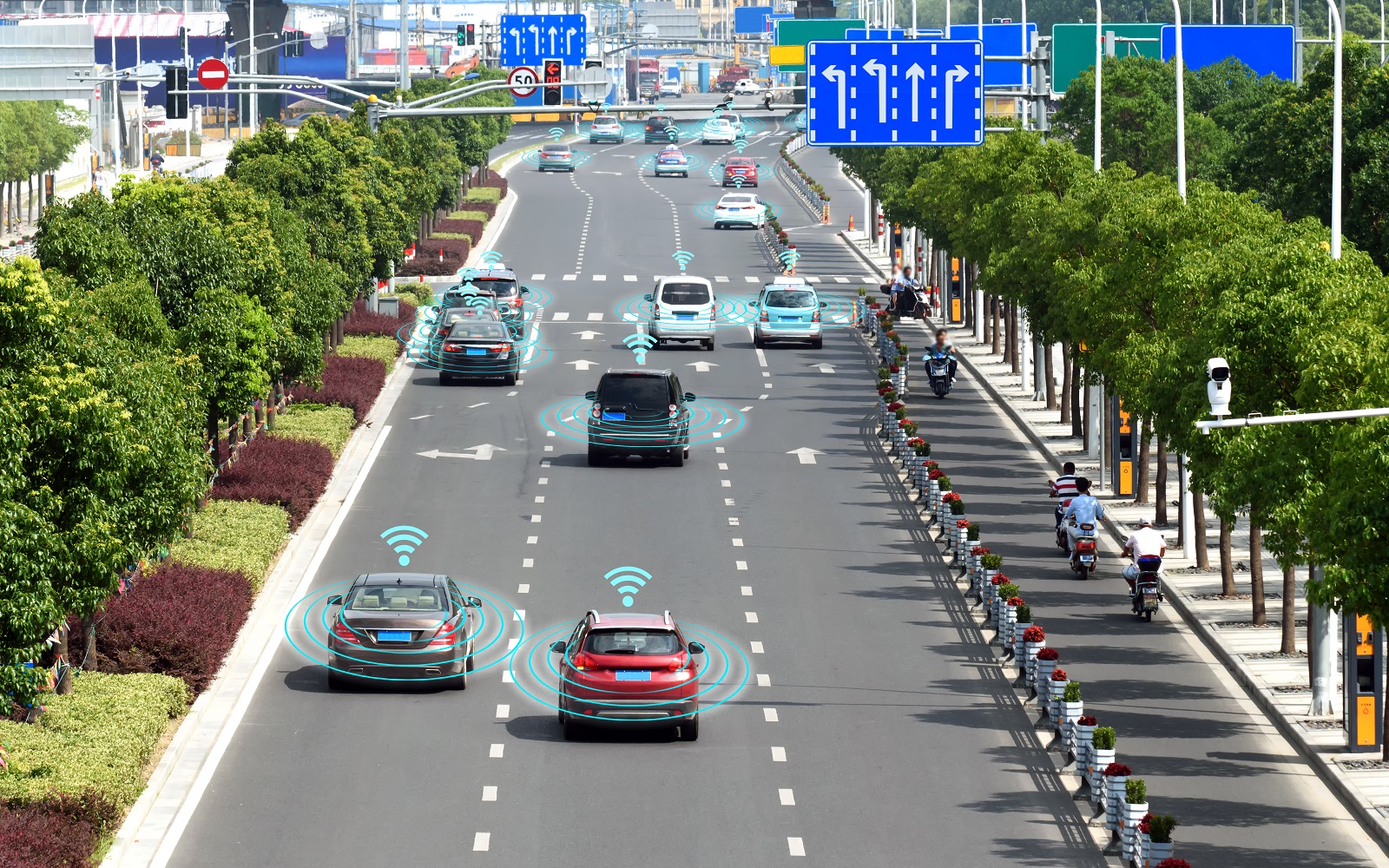

In the context of virtual reality and the industrial metaverse, it is common to talk about autonomous vehicles that communicate with each other in real time, among other things. Testing their operation in a real, on-road environment requires appropriate infrastructure and involves many risks that many road administrators are unwilling to take. Thanks to the industry metaverse, such vehicles can be safely tested in all sorts of real-world environments and traffic situations even before the first test vehicle hits the road.
Virtual showroom
The ability to visualize the vehicle, how it works or which modifications are available, is also an excellent way to present the offer to the customer, who will be able to see and “touch” the car, or even go for a test drive and check it out in any environment of their choice – their own city or even another continent. This opens up new avenues of product development that would be hard to explore in a traditional test environment.
Virtual car workshop
Digital twin and metaverse technology could revolutionize the way smart cars are serviced and repaired. Based on the digital twin, mechanics will not only be able to determine with high probability what might have broken down in a particular car model, but also diagnose it correctly based on readings from sensors placed in the actual vehicle. This way, the workshop will be able to order the right parts even before the actual damaged car arrives. On the other hand, in case of software errors, any defects will be able to be fixed remotely.
The metaverse and the development of the virtual factory concept
The metaverse has contributed to the development of the concept of a “virtual factory”, where all stages of car production are simulated in a virtual environment. Above all, this technology makes it possible to identify and solve potential problems and optimize processes even before actual series production begins. One example of such deployments is BMW's next-generation electric car factory in Debrecen, Hungary. The production facility, which is not expected to be built until 2025, already exists in virtual reality. Using NVIDIA's digital tools, a highly detailed simulation was created, covering the entire production process including robot targets and operator stations. This way, all relevant operations were verified in the metaverse even before construction of the project began. The virtual factory is just the beginning of a complete digital manufacturing world that includes other smart factories, as well as the necessary tools and applications from third-party sub-suppliers to design the appearance of cars, building structures and logistics planning, among others.
How to implement the metaverse concepts in manufacturing for the automotive sector?
In the automotive industry, demand for the metaverse technology solutions continues to grow. The estimated market value of this sector is between $1.4 and $5 billion, and the cumulative annual growth rate is as high as 40%. Implementing the metaverse in manufacturing processes requires investment in VR technology, training employees and developing partnerships with the metaverse technology providers. Companies that decide to use this technology must clearly define the goals, benefits and added value for customers that comes from its use. Already today, most auto parts manufacturers are using solutions specific to the metaversum, such as computer-aided design (CAD), sensors that take analytical data from real-world cars, and CAE software to create simulations using digital twins. And from that stage, it's not far to the creation of realistic meta-worlds where digital car models become tangible reality.
Knauf Automotive's offer includes not only plastic injection molding or foamed plastic molding technology, but also a full range of consulting service, design and optimization of automotive components based on numerical simulations and state-of-the-art 3D scanners. We are able to realize even very complex projects with injection molding as well as support with our plastics processing expertise the development of eco-friendly vehicles of the future.
Advantages and risks of the metaversum – what might the future bring?
Like any new technology, the metaversum creates both opportunities and some risks. One of the promising directions of its development is the application of artificial intelligence to create optimal scenarios for the operation of manufacturing plants, taking into account lean supply chain concepts, logistics systems and even entire transportation systems based on fully autonomous vehicles. In such a virtual world, both car manufacturers and their sub-suppliers can operate transparently, for example, through the use of blockchain, a virtual supply chain. The risks include those that traditionally accompany IT development, such as cybercrime and threats related to security and data protection. Nonetheless, metaverse manufacturing appears to be a very promising path for the automotive sector.