Until recently, the primary argument against buying an electric car were the limited ranges of such vehicles. Today they can reach up to 700 km, so they may in fact sometimes be compared even with the ranges of combustion cars. However, it is worth remembering that this parameter depends on many different factors, which are related not only to the way the vehicle is operated.
Which electric cars have the longest range?
Electric cars are becoming less and less different from internal combustion vehicles in terms of power, speed, as well as range. The lithium-ion batteries for electric cars produced today keep the ranges of electric cars at no less than 400 km. Electric cars with the longest ranges can, according to manufacturers' declarations, drive even more than 700 km on a single charge, which corresponds to the route from Warsaw to Vienna. Which electric cars have the longest ranges? At the top of the rankings appear brands such as Mercedes, BMW and Tesla, but it is worth remembering that the figures given by manufacturers are the result of laboratory tests conducted under specific conditions. How many kilometers without recharging an electric car can be driven in practice is determined by factors such as the way of driving, terrain, how loaded the car is and even climatic conditions.
Factors affecting the actual range of an electric car
As you know, the energy requirements of a car are not the same in all conditions and are constantly changing. So what does the range of an electric car depend on? Experienced drivers know that driving style is of great importance, but not only. First, in all vehicles increased energy consumption in general is affected by dynamic acceleration and deceleration. Thus, a guarantee of increased time between recharges of an electric car will be smooth driving at relatively low speeds, such as in the city. However, there are also factors beyond the driver's control, which are the vehicle's own weight, the number of passengers and cargo carried, the weight of the batteries or the terrain. The rules are simple – the heavier the car and the more uphill climbs it has to overcome, the faster the battery will need to be recharged. A characteristic feature of electric cars is also the large impact of air conditioning operation. The heating and cooling system consumes a great deal of energy stored in the battery, so the real range of electric cars, especially in winter, will be considerably less than in seasons with moderate temperatures.
How much does it cost to replace the battery in an electric car and when does it need to be done?
Despite the fact that newer and newer generation batteries are being used in electric cars, every battery ages over time and loses its capacity. The whole process involves the gradual deactivation of successive damaged cells, as a result of which the battery can store less and less energy, necessitating more frequent recharges. Today, manufacturers estimate the battery life of an electric car at about 900 cycles of full charging, which can also be measured as several shorter charges giving a total of 100%. This number of cycles should be enough for about 240-300 thousand kilometers, which is estimated to be equivalent to 20-25 years of operation with normal use of the car with average frequency. The phenomenon of a sharp reduction in the range of electric cars happened only with older models and was due, for example, to the lack of an active battery cooling system, which is now standard in new vehicles. However, if the capacity of the battery is so small that it does not allow normal use of the car, it is worth considering its regeneration. This is because replacing the battery with a new one today involves a very high cost of up to 20 thousand euros.
Can the EV range be extended?
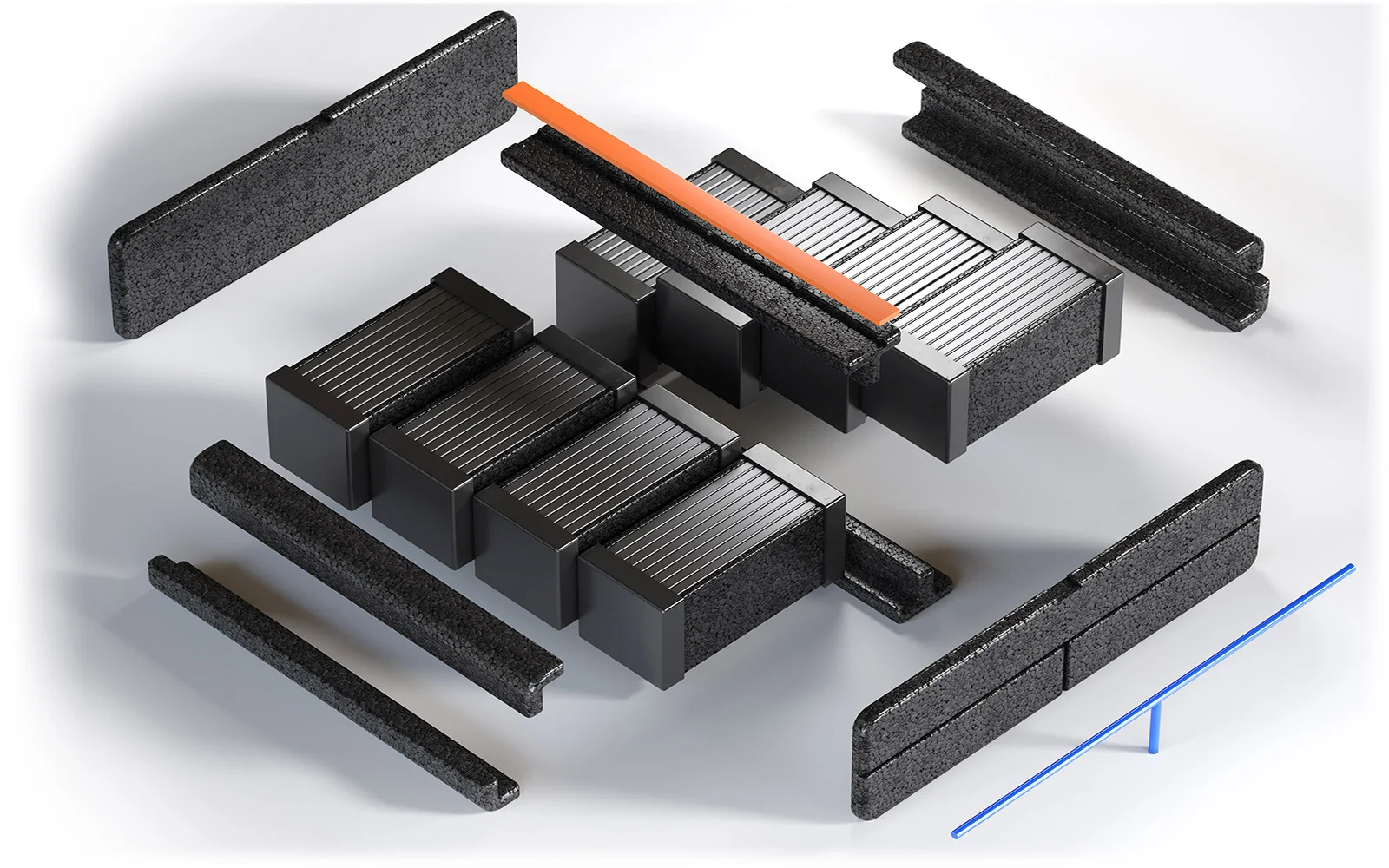
The current range of electric cars is large enough that in most cases they can be taken comfortably on a long trip. What remains problematic, however, is the limited access to chargers. They are still a rarity on non-urban routes or in smaller towns, while there are increasingly long queues to those installed in large cities, which significantly reduces the convenience of using electric cars. Until the charging infrastructure is widely available and as common as traditional fueling stations, it remains for manufacturers to work on further increasing the range of electric cars. Drivers, on the other hand, need to use their cars skillfully to enjoy ranges as close as possible to the factory range. In this context, they are often advised, for example, to have limited heating of the cabin during the winter season or to choose a heat pump instead of a traditional heater, which draws large amounts of energy needed for heating directly from the battery. At the same time, manufacturers are working on different types of batteries for electric cars, more efficient systems to ensure ideal operating conditions or solutions to protect sensitive cells from damage. The material used more and more in this regard, for example, is EPP foamed polypropylene.
The role of plastic components in increasing the range of electric cars
Parts molded from EPP foamed plastic are conquering the electric car manufacturing sector due to their unique properties. Among other things, they make it possible to achieve the effect of reducing the weight of the body, while at the same time perfectly absorbing shocks, providing excellent thermal insulation and prolonging the life of the components. Filled to 95% with air, EPP material is not only extremely lightweight, but also very strong and resistant to deformation. As a result, it finds a range of applications in the areas of passive safety systems, seat fillings, cabin insulation or electric car battery production. For example, foams for insulating battery packs for industry extend the life of cells, protecting them from extreme temperatures, mechanical damage or electrical malfunctions. EPP is an innovative material that continues to find new and more interesting applications in the automotive sector, improving the range of electric cars, but also allowing combustion cars to comply with increasingly stringent exhaust standards.