In recent years, electromobility has become an integral part of the discussion on the future of transportation. However, it is worth noting that electric vehicles work in a completely different way than combustion cars. What is there to know about the subject?
How is an electric car built?
The design of electric cars differs significantly from the design of combustion engine vehicles, which until recently completely dominated our roads. These differences are mainly due to the characteristics of the drives used in electric cars. The most important component here is the battery, which provides the necessary energy – lithium-ion batteries are most often used for this purpose. Their widespread use is primarily due to their high-energy density, long service life and relatively low weight.
How does an electric car work? In the case of such vehicles, the operation of the engine is based on the conversion of electrical energy into mechanical energy. The drive of an electric car can be located at the front or in the rear; it is also common practice to use several drives simultaneously. Importantly, both the battery and the motor generate large amounts of heat during operation – therefore, effective cooling of these components is vital. A properly sized cooling system ensures that all parts maintain the proper operating temperature, which is crucial for driving performance and vehicle durability.
Another key component is the control system, which manages the flow of energy between the battery and the electric motor, ensuring optimal efficiency and performance of the vehicle. Energy regenerative brakes are also often used in such cars. Their task is to convert kinetic energy into electrical energy, charging the battery – a process that helps increase driving range and improve energy efficiency.
Does an electric car have a clutch?
Significant differences can also be seen in terms of engine gearboxes. While a gearbox with several positions is standard in internal combustion vehicles, electric cars do not need such a mechanism. Instead, a very simple transmission with one gear and no clutch is used – this is because the torque of the electric motor is available from zero rpm. The exception, however, are some electric sports vehicles, which can benefit from more elaborate configurations.
How does the drive of an electric car work?
Electric car propulsion is a complex system that is responsible for the movement of the vehicle by converting the electricity stored in the batteries. The key element of this system is the inverter – its task is to convert the DC current from the batteries into an alternating current suitable for motor operation. What is more, this component controls the speed and torque of the vehicle by changing the voltage and frequency level of the current supplied to the drive unit.
The conversion of electrical energy into mechanical motion is carried out using an electromagnetic effect. A typical motor design includes two basic components that play a key role in this process:
- a rotor with a winding powered by electricity;
- a stator where magnetic fields are generated, which causes the rotor to rotate, thus propelling the vehicle.
See also: Production of foamed plastic elements – foams for battery packs for the automotive industry.
Electric car propulsion and performance
Electric motors are characterized by high torque available right from the start of driving, which translates into a quick and smooth response of the vehicle to the accelerator pedal. Compared to internal combustion engines, which take time to reach full power, electric motors offer an immediate response – contributing to a more dynamic driving experience. In addition, the electric drive has a very wide operating range, meaning it can deliver high power even at very low speeds. This is particularly important in urban driving, when a quick response to changes in the traffic situation is often required.
The performance of an electric car depends mainly on the efficiency of the entire drivetrain, including the battery, inverter and electric motor. The more efficiently these components work together, the better performance can be achieved with optimal energy efficiency.
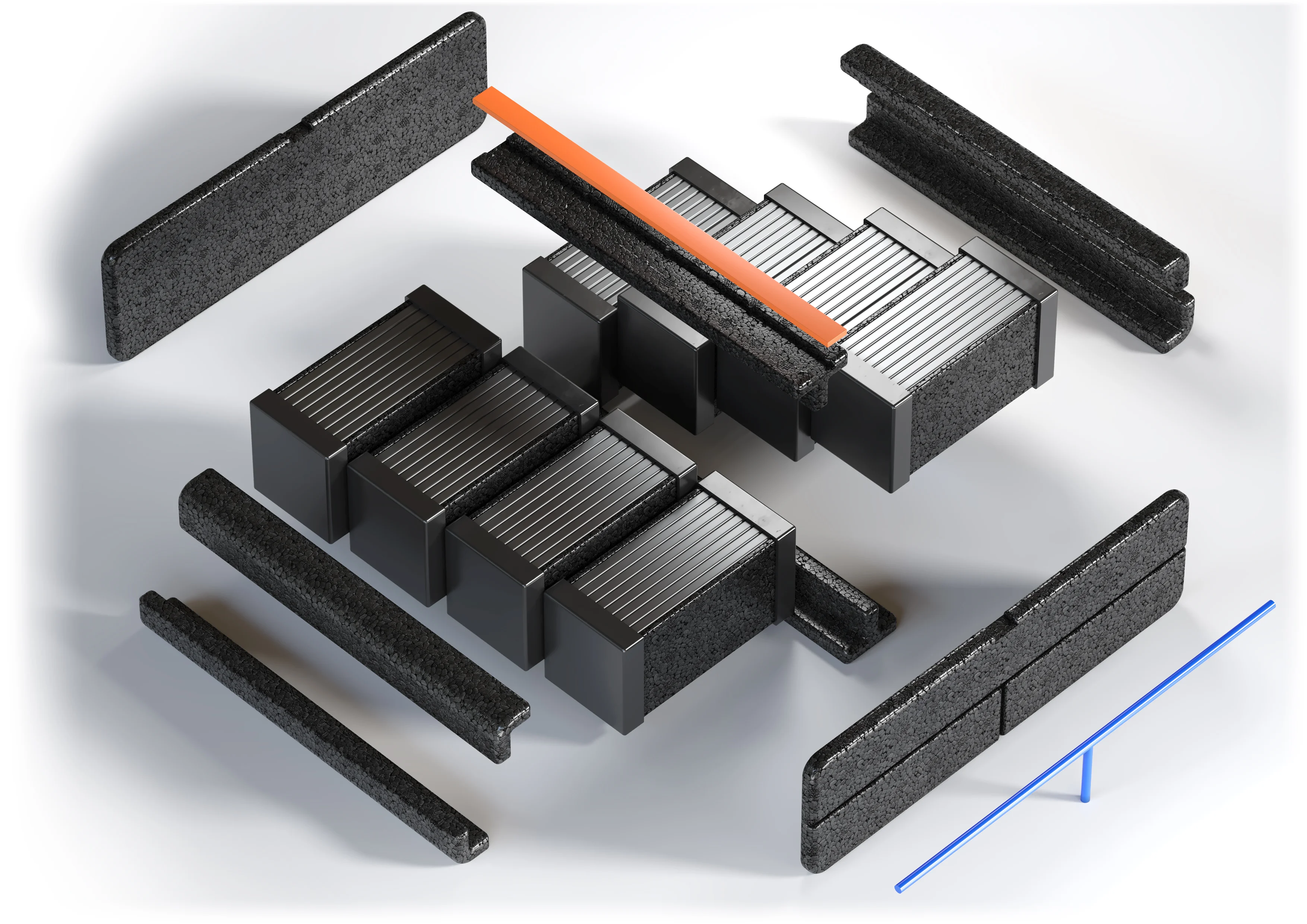
EPP components in electric car design
The battery, as the heart of any electric car, must be properly protected. For this reason, the materials used to make a car battery housing should meet a number of stringent requirements in terms of impact resistance, thermal insulation and resistance to fire and electrical breakdown. It is also essential to keep the weight low enough so that the components used do not adversely affect engine performance. Durability, insulation and low weight are features you can count on when choosing foamed polypropylene (EPP), for example.

EPP is a material used in many areas of the automotive industry – from the manufacture of packaging to the creation of shock protection components or parts of car equipment. Due to its properties, foamed polypropylene can effectively replace other plastics and in certain cases even aluminium parts. EPP products are one of the cornerstones of Knauf Automotive's offer – we are a trusted supplier for many companies in the automotive sector that opt for efficient, sustainable and innovative solutions.