Many drivers still have no confidence in electric cars, mainly because of their range. In practice, it has been proven, however, that batteries for electric cars can travel far more kilometres than estimated. The technologies and materials used by the manufacturers can ensure ideal working conditions for the battery and extend its life.
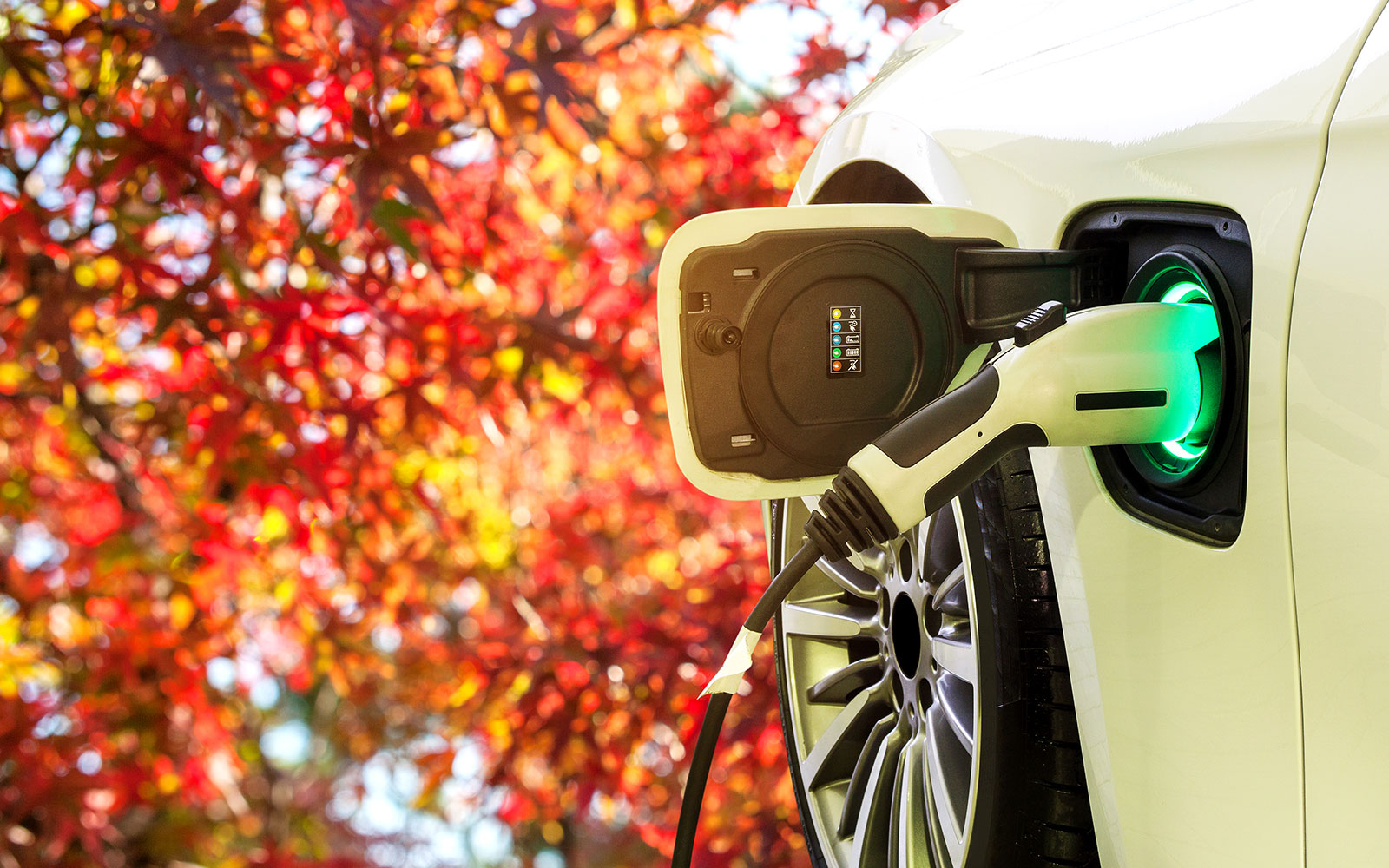

The most common doubts relating to electric car technology concern purely operational issues. The lithium-ion batteries used in them have a defined capacity, which gradually decreases as time passes and subsequent charging cycles follow. Consequently, the battery is connected to the car charger more and more frequently, and finally it needs replacement, which is quite expensive. However, the experience of using electric cars in the United States and Europe, among others, shows that the life of a car battery has exceeded the expectations of manufacturers and users themselves. And although electric cars are not as good as internal combustion engine vehicles in terms of range, their sales are growing every year.
In addition, vehicle manufacturers and technology suppliers are working on new design and material solutions to ensure optimal battery conditions and thus extend the life cycle of batteries. Knauf Industries has also joined the competition with the introduction of the car battery pack, which includes insulation components from the innovative EPP foam material.
How long does the battery last in an electric car?
Many myths have been rumouring about the short life of electric car batteries for a long time, which were based on the experience of using popular lithium-ion batteries in smartphones and laptops. It is commonly known that each charging cycle reduces the capacity of the battery, i.e. the amount of energy stored in it to power the device. Today, electric cars are already in use for so long that real data on the durability of the batteries used in them can be quoted. For example, Plug In America had tested Tesla S and it was found that after the first 80 000 km the cells lost about 5% of their capacity. Later on, the drop in factory parameters is much slower. The manufacturer gives an 8-year warranty on the cells used, and estimates their life at 500 000 – 800 000 km. Renault and Hyundai offer the same warranty, but in these cases the mileage limits are a little lower, at 160 000 km and 200 000 km respectively.
In most cases, a battery is replaced under warranty if its capacity drops below 60-70% of its original value. It is worth noting that the average European driver drives about 37 km a day, which gives about 12-14 years of stress-free use in the case of Renault and Hyundai, and in the case of Tesla, even up to 60 years! In practice, there are electric cars in Europe and the United States, which have already exceeded the barrier of up to half a million kilometres driven, and their battery capacity has not decreased below 80%. The life of the cells can be further extended by means of appropriate use and working conditions.
What does the life of a car battery depend on?
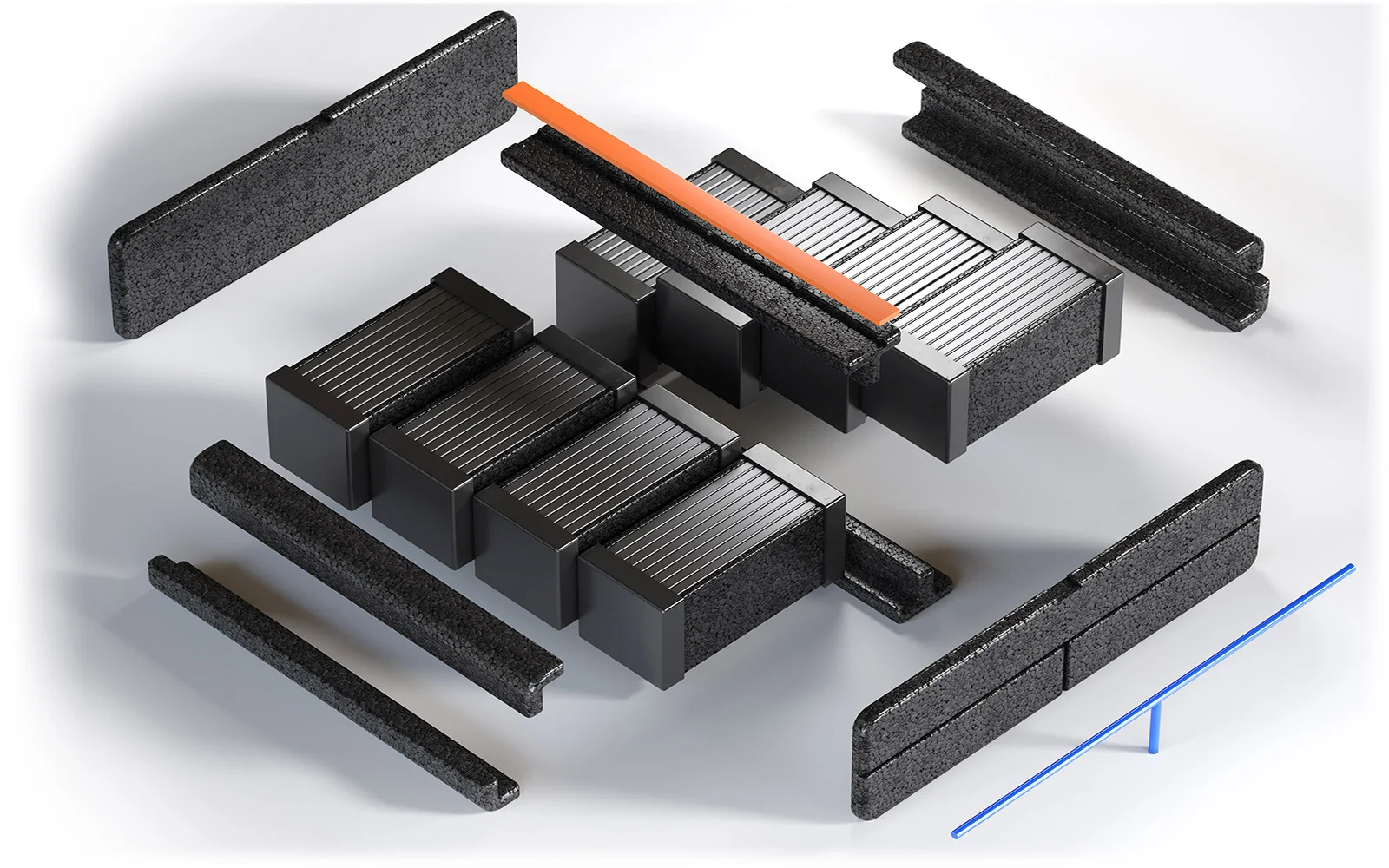
The durability of a battery depends on its construction and operating conditions. The greatest enemies of lithium-ion batteries are particularly the heat, which causes them to overheat and significantly reduce their capacity. This problem was particularly present in the first models of electric cars with a passive air cooling system. Today, battery units are most often equipped with active liquid cooling and heating systems. In addition, the power distribution control computer ensures that the battery for the electric car operates within optimal charging ranges of 20-80%. Battery life is also adversely affected by long periods of downtime during which the batteries are not recharged, as well as by fast charging, which is confirmed by the experience of European and American taxi drivers. It is also worth bearing in mind that the battery is exposed to various types of shocks and vibrations, which in the worst case can lead to its damage. That this is why it also depends so much on the construction of the battery pack, and in particular on the materials for its insulation.
Why is it worth to use battery insulation systems for electric cars?
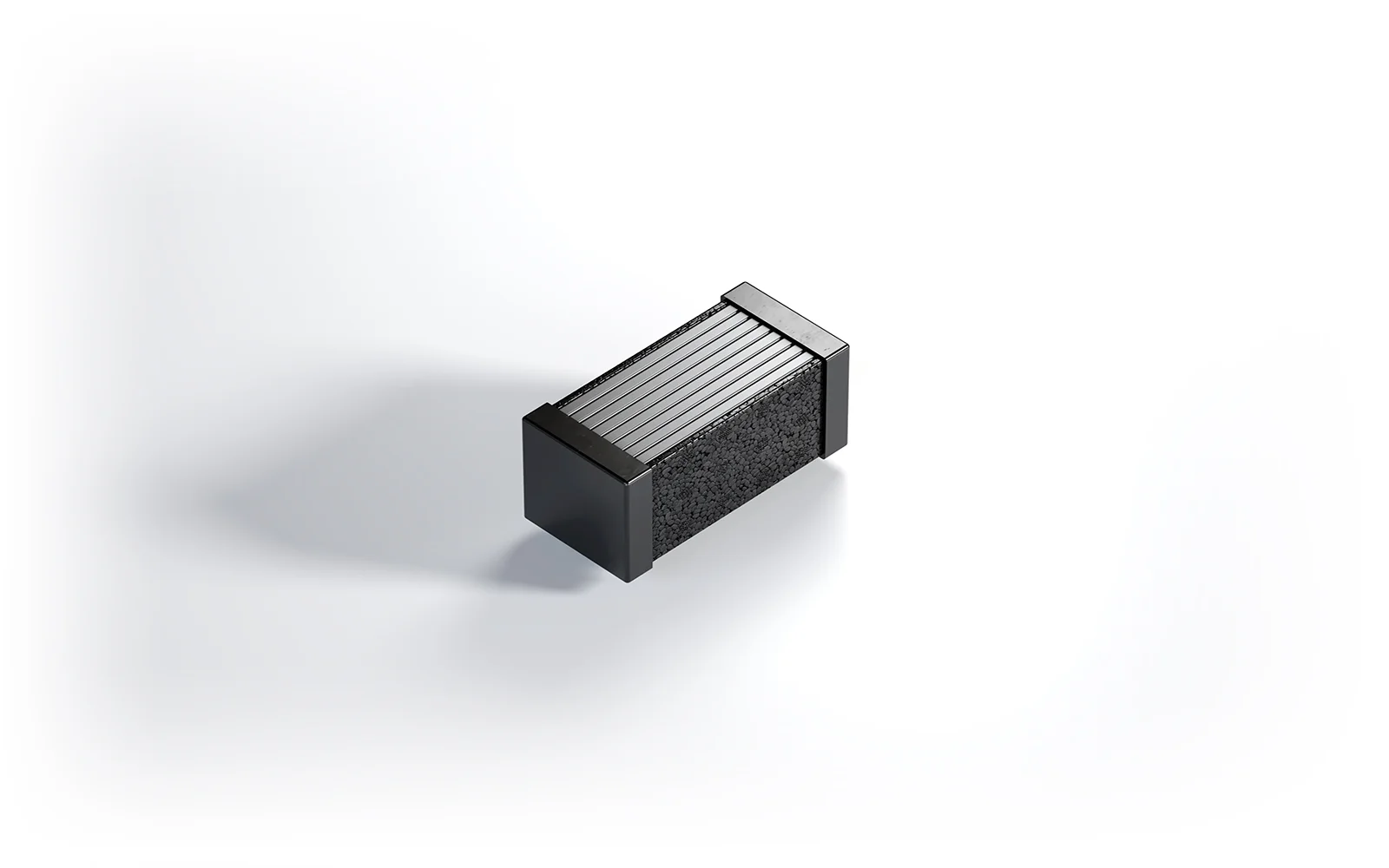
Each charging leads to a chemical change, which can result in an increase in the size of the cells and even a deformation of the battery for the electric car. It can generate problems with effective temperature regulation, temperature rise and penetration into adjacent cells. That is why proper insulation of battery cells is so important. Properly selected materials will, on the one hand, separate them in terms of thermal and electrical properties and, on the other hand, protect the cells and electrical connections from deformation or mechanical damage in difficult conditions of use. Very effective material used in the construction of the battery for electric cars has proved to be the expanded polypropylene foam (EPP) produced by Knauf Industries, which is used in the production of car components. They provide both effective thermal and electrical insulation. They are very resistant to high temperatures that can occur during fast charging, as they meet UL94 requirements. Their added value, which is very much appreciated by the automotive industry, is the low weight, which allows the construction of car batteries to “slimming down” and thus reducing the actual weight of electric vehicles, which also increases their range.
Read also: How COVID-19 will influence development of electric and autonomous cars?
What types of insulation for car batteries with EPP?
One of the types of EPP foam insulation are battery cell separators, which not only absorb shocks, but also prevent the cells from deformation due to chemical changes. The expanded polypropylene is ideal in this case as it does not undergo permanent deformation and returns to its original shape. This is an excellent thermal insulator, which prevents temperatures from passing between the battery components and the electric car, ensuring even temperature distribution. The components manufactured from this material also have a high breakdown voltage value and prevent uncontrolled short circuits between the individual battery cells. This is why expanded polypropylene is also ideal for the production of components that act as a cable clamping rail.
EPP foams are very flexible, resistant to breaking and crumbling and thus provide a secure fixing of the cabling. Fixings made of expanded plastic significantly facilitate the process of conducting electrical connections, eliminating the need to use e.g. screw connections. The individual components are quickly and easily connected with a latch. These new material solutions have the potential to revolutionise the electromobility industry. They increase the life and durability of the battery for an electric car, while at the same time increasing the safety of its operation, which will have a remarkable impact on the even greater popularisation of EV technology in the near future.